Eddy covariance measurements and parameterisation of traffic related particle emissions in an urban environment
Abstract. Urban aerosol sources are important due to the health effects of particles and their potential impact on climate. Our aim has been to quantify and parameterise the urban aerosol source number flux F (particles m−2 s−1), in order to help improve how this source is represented in air quality and climate models. We applied an aerosol eddy covariance flux system 118.0 m above the city of Stockholm. This allowed us to measure the aerosol number flux for particles with diameters >11 nm. Upward source fluxes dominated completely over deposition fluxes in the collected dataset. Therefore, the measured fluxes were regarded as a good approximation of the aerosol surface sources. Upward fluxes were parameterised using a traffic activity (TA) database, which is based on traffic intensity measurements.
The footprint (area on the surface from which sources and sinks affect flux measurements, located at one point in space) of the eddy system covered road and building construction areas, forests and residential areas, as well as roads with high traffic density and smaller streets. We found pronounced diurnal cycles in the particle flux data, which were well correlated with the diurnal cycles in traffic activities, strongly supporting the conclusion that the major part of the aerosol fluxes was due to traffic emissions.
The emission factor for the fleet mix in the measurement area EFfm=1.4±0.1×1014 veh−1 km−1 was deduced. This agrees fairly well with other studies, although this study has an advantage of representing the actual effective emission from a mixed vehicle fleet. Emission from other sources, not traffic related, account for a F0=15±18×106 m−2 s−1. The urban aerosol source flux can then be written as F=EFfmTA+F0. In a second attempt to find a parameterisation, the friction velocity U* normalised with the average friction velocity ![]() has been included, F=EF
has been included, F=EF 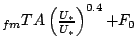 . This parameterisation results in a somewhat reduced emission factor, 1.3×1014 veh−1 km−1. When multiple linear regression have been used, two emission factors are found, one for light duty vehicles EFLDV=0.3±0.3×1014 veh−1 km−1 and one for heavy-duty vehicles, EFHDV=19.8±4.0×1014 veh−1 km−1, and F0=19±16×106 m−2 s−1. The results show that during weekdays ~70–80% of the emissions came from HDV.
. This parameterisation results in a somewhat reduced emission factor, 1.3×1014 veh−1 km−1. When multiple linear regression have been used, two emission factors are found, one for light duty vehicles EFLDV=0.3±0.3×1014 veh−1 km−1 and one for heavy-duty vehicles, EFHDV=19.8±4.0×1014 veh−1 km−1, and F0=19±16×106 m−2 s−1. The results show that during weekdays ~70–80% of the emissions came from HDV.





