the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
Tracer-based source apportioning of atmospheric organic carbon and the influence of anthropogenic emissions on secondary organic aerosol formation in Hong Kong
Yubo Cheng
Yiqiu Ma
Here we conducted comprehensive chemical characterization and source apportionment of 49 PM2.5 samples collected in Hong Kong. Besides the major aerosol constituents, 39 polar organic species, including 14 secondary organic aerosol (SOA) tracers of isoprene, monoterpenes, β-caryophyllene, and naphthalene, were quantified using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS). Six factors, i.e., SOA, secondary sulfate (SS), biomass burning (BB)/SOA, sea salt, marine vessels, and vehicle emissions, were apportioned by positive matrix factorization (PMF) as the major sources of ambient organic carbon (OC) in Hong Kong. The secondary formation, including OC from SOA, SS, and aging of BB plume, was the leading contributor to OC (51.4 %, 2.15 ± 1.37 µg C m−3) throughout the year. We then applied a tracer-based method (TBM) to estimate the SOA formation from the photo-oxidation of four selected precursors, and monoterpene SOA was the most abundant. A Kintecus kinetic model was used to examine the formation channels of isoprene SOA, and the aerosol-phase ring-opening reaction of isoprene epoxydiols (IEPOXs) was found to be the dominant formation pathway. Consistently, IEPOX tracers contributed 94 % to total GC–MS-quantified isoprene SOA tracers. The TBM-estimated secondary organic carbon (SOCTBM) and PMF-apportioned SOC (SOCPMF) showed similar temporal trends; however, SOCTBM only accounted for 26.5 % of SOCPMF, indicating a large fraction of ambient SOA was from other reaction pathways or precursors. Results of Pearson's R and multivariate linear regression analysis showed that NOx processing played a key role in both daytime and nighttime SOA production in the region. Moreover, sulfate had a significant positive linear relationship with SOCPMF and SS-related SOC, and particle acidity was significantly correlated with SOC from the aging of BB.
- Article
(959 KB) - Full-text XML
- BibTeX
- EndNote
Organic aerosol (OA) is a significant component of ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5). It accounts for 20 %–60 % of the total PM2.5 mass on a global scale (Kanakidou et al., 2005; Van Dingenen et al., 2004; Zhang et al., 2007) and even up to 90 % in rural areas (Kanakidou et al., 2005; Zhang et al., 2007). OA is either directly emitted into the atmosphere from natural (e.g., vegetative detritus, volcano activity) and anthropogenic sources (e.g., biomass burning (BB), vehicle exhaust, and cooking) or secondarily formed through the oxidation of biogenic and anthropogenic gas-phase precursors and the subsequent partition process or particle-phase reactions (Gelencsér et al., 2007; Hildemann et al., 1996; Hu et al., 2010; Zheng et al., 2014). Given the varying emission sources, meteorological conditions, and anthropogenic activities worldwide as well as their influences on ambient OA composition, aerosol scientists have put lots of effort into investigating the atmospheric processes of OA and their primary and secondary sources, which aid the development of more targeted control policies of PM2.5 pollution (Hu et al., 2010; Huang et al., 2014; Schauer et al., 2007; Simoneit, 1999; Zheng et al., 2005). Huang et al. (2014) applied positive matrix factorization (PMF) to apportion the sources of OA at four urban locations in China, i.e., Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Xi'an. They found that secondary formation accounted for a predominant fraction of OA (44 %–71 %) at all four sites. Hong Kong, a megacity located on the southern coast of China in the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region and a hub port for the southern Asia-Pacific region, has its unique organic carbon (OC) source characteristics. Hu et al. (2010) incorporated biogenic and anthropogenic SOA tracers and some primary organic aerosol (POA) markers into PMF and identified seven OA sources in Hong Kong. They found that 45 % of OC in Hong Kong during summertime was from secondary formation, and the number could reach up to 65 % on sampling days under regional pollution from the PRD area.
All these studies have illustrated the importance of secondary formation to OA in the ambient atmosphere. However, due to SOA's complex chemical composition and formation mechanisms, a precise prediction of SOA load from individual precursors at both regional and global scales is still challenging. An SOA tracer-based method (TBM) has been developed to partially solve this problem, which estimates the amount of SOA and secondary organic carbon (SOC) formed from the atmospheric oxidation of selected VOCs (i.e., isoprene, monoterpenes, β-caryophyllene, toluene, and naphthalene) using the mass ratios of tracer-to-SOA/SOC obtained from laboratory smog chamber experiments (Kleindienst et al., 2007, 2012). However, TBM can only capture SOC formation from the above-listed VOC precursors, and it may underestimate the actual SOC levels in the ambient atmosphere due to the lack of SOA tracer-to-SOC ratio values of a broader range of OA precursors. Therefore, besides the SOA tracer-based method, we have also applied PMF to evaluate the contributions of SOC and primary emissions to OA in the region.
Many studies have reported the observational evidence of biogenic SOA enhancement induced by anthropogenic emissions, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulfur dioxide (SO2) (Huang et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2015; Rattanavaraha et al., 2016). NOx is one of the critical drivers of SOA formation through the photochemical oxidation of VOCs via peroxy radical pathways (Finlayson-Pitts and Pitts, 2000). Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) reacts with ozone (O3) to form an NO3 radical, a critical nighttime gas oxidant. Several laboratory studies have reported high SOA yields from the oxidation of biogenic VOCs (BVOCs) by NO3 radical (Fry et al., 2009; Ng et al., 2008). Some field studies also revealed that SOA formation from NO3 oxidation of BVOCs occurs during both daytime and nighttime (Brown et al., 2013; Rollins et al., 2013). The effect of SO2 on SOA formation was often explained in the context of particle acidity in laboratory studies, which promotes SOA production through acid-catalyzed heterogeneous reactions (Jang et al., 2002; Surratt et al., 2010). Sulfate was also suggested to enhance isoprene-SOA formation by acting as the nucleophiles, providing active aerosol surface area, and through the salting-in effect (Rattanavaraha et al., 2016; Xu et al., 2015). Recently, Wang et al. (2016) proposed a new sulfate formation pathway in aqueous aerosols through NO2 oxidation and ammonium neutralization, and synchronous enhancements of both nitrate and SOA production in aqueous aerosols were reported. These laboratory and field monitoring studies have shown that the abundance and chemical nature of ambient OA are significantly influenced by the complex interactions among source emissions, anthropogenic activities, atmospheric physical or chemical processes, and meteorological conditions (An et al., 2019).
In this study, we collected 49 PM2.5 samples at an urban site in Hong Kong during a whole year period. Concentration levels of 39 polar organic species were quantified using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS), and their temporal and meteorological variations were evaluated. With the input of SOA tracers and primary source markers into PMF, we quantitatively assessed the contributions of various primary and secondary sources to OC. SOC formed from individual biogenic (i.e., isoprenes, monoterpenes, and β-caryophyllene) and anthropogenic VOCs (i.e., naphthalene) were estimated using the TBM. Finally, the impacts of anthropogenic pollutants (e.g., NO2, O3, NO3, SO2, and tropospheric odd oxygen (Ox)) and PM2.5 constituents (e.g., sulfate, acidity, and liquid water content) on total and individual SOCs estimated by both TBM and PMF were evaluated using Pearson's R analysis and multilinear regression model. This study provides comprehensive information on the sources of OA and SOA in Hong Kong as well as direct evidence of anthropogenic influences on the SOA formation in the region, which may serve as the scientific basis for the formulation of the PM2.5 mitigation policy in the region.
2.1 Sample collection
The PM2.5 samples were collected on the 12th floor of Science Tower in the campus of Hong Kong Baptist University (114∘15 E, 22∘13 N; ∼40 m above the ground), which is a typical urban site. PM2.5 samples were collected from 6 September 2011 to 16 August 2012, and a total of 49 samples were collected. A high-volume air sampler was used to collect PM2.5 onto a quartz fiber filter (20 cm×25 cm) at a flow rate of 1.13 m3 min−1 for 24 h. The quartz fiber filters were prebaked at 550 ∘C for 24 h to remove organic contaminants. After sampling, the filters were immediately transferred to the laboratory and stored at −18 ∘C until analysis.
2.2 Chemical analysis
For elemental carbon (EC) and OC analysis, a 1×1 cm2 filter was cut and analyzed using a thermal and optical transmittance aerosol carbon analyzer (Sunset Laboratory, Tigard, OR, USA). Major ions (i.e., Cl−, NO, SO, C2O, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, NH) were identified and quantified by ion chromatography (IC, DX500, Dionex, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Vanadium (V) and nickel (Ni) were analyzed using an Agilent 7900 ICP-MS (inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer). Detailed analytical methods for the measurements of EC, OC, and ions were described in our previous work (Hu and Yu, 2013; Ma et al., 2019).
Thirty-nine polar organic species were identified and quantified using an Agilent 7890A-5975C GC–MS with prior BSTFA derivatization (N, O-bis-(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide, with 1 % trimethylchlorosilane, TMCS). For each aerosol sample, 20 cm2 of the filter was cut into small pieces and sonicated for 10 min with 10 mL of distilled acetonitrile (HPLC grade); the extraction was repeated three times. The extracts were combined and filtered through a Millipore 0.45µm PTEE hydrophobic Teflon filter into a 50 mL round flask, concentrated to ∼0.5 mL by rotary evaporation, and transferred into a 5 mL reaction vial. The round flask was rinsed with 1 mL of acetonitrile three times, and the rinsing solvent was transferred into the reaction vial as well. The final extract was blown to dryness under a gentle stream of pure nitrogen gas at 40 ∘C and then derivatized with 100 µL of BSTFA and 50 µL of pyridine at 70 ∘C for 2 h. After the reaction vial cooled down to room temperature, 30 µL of tetracosane-d50 (internal standard, 50 µg mL−1 in hexane) was added. The derivatives were analyzed by GC–MS. Two microliters of the derivatized sample or standard were injected and separated on an HP-5MS capillary column (, Agilent J&W). The temperature program and instrument settings were adapted from the method used by Hu et al. (2008).
Table 1Concentrations of 14 SOA tracers, 25 polar organic compounds, and 9 inorganic ions in PM2.5 collected in Hong Kong under three meteorological conditions.
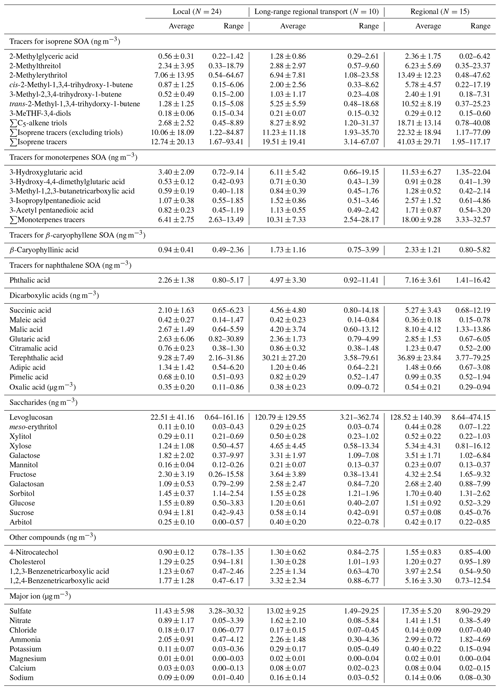
Saccharides, di- and tricarboxylic acids, 4-nitrocatechol, and cholesterol were identified and quantified using authentic standards. The SOA tracers were identified using surrogate compounds with similar structures and functional groups (Hu et al., 2008; Hu and Yu, 2013), and the detailed information is provided in Table 1. Recovery tests of these organic species were carried out by spiking the mixture of standards onto blank quartz filters, followed by the same sample extraction and analysis processes. Recoveries of the polar compounds were within the range of 80 % to 120 %. Analysis of hopanes has been reported in our previous study (Ma et al., 2019). Four hopanes, including 17α,21β-hopane, 17α,21β-22R-homhopane, 17α,21β-22S-homhopane, and 17α,21β-30-norhopane, were measured using an Agilent 6890N-5975 GC–MS with the thermal desorption (TD) method. Recoveries of four hopane standards ranged from 83 % to 98 %.
Hourly meteorological and air quality data (i.e., temperature, relative humidity (RH), O3, SO2, and NO2) in the vicinity of the sampling site were collected by Hong Kong Environmental Protection Department (HKEPD) (http://envf.ust.hk/dataview/gts/current/, last access: 16 June 2021). During the sampling period, the ambient temperature ranged from 14.52 to 31.01 ∘C, with an annual average of 24.17 ± 5.00 ∘C. The daily average of RH ranged from 52.94 % to 97.02 %, with a yearly average of 79.87 ± 10.54 %. Heavy rains are common in Hong Kong during summer, which effectively washes out the PM pollutants.
Hong Kong is located at the southeast edge of the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region. PRD is a rapidly developing area with intensive industrial activities. As described in our previous studies on the analysis of humic-like substances (HULISs) and water-soluble PM2.5-induced oxidative potential using the same set of PM2.5 samples (Ma et al., 2019; Cheng et al., 2021), we carefully examined the air mass backward trajectories and categorized all sampling days into three groups, i.e., days mainly influenced by the regional pollution from the PRD region (regional days), days influenced by long-range regional transport of air mass from the northern and eastern China (LRT days), and days dominated by the locally generated pollutants (local days). The concentration levels of both PM2.5 and O3 and the spatial distribution patterns of SO2 over the 18 Hong Kong air quality monitoring stations (http://envf.ust.hk/dataview/gts/current/, last access: 16 June 2021) on each sampling day were also checked to assist the classification. A summary of the classification of sampling days and the typical air mass backward trajectories under the three meteorological categories are presented in Table S2 and Fig. S2 in Ma et al. (2019), respectively.
Table 2PMF and TBM-apportioned OCs, concentrations of gas pollutants, PM2.5, EC, OC, and major aerosol characteristics under different meteorological conditions.
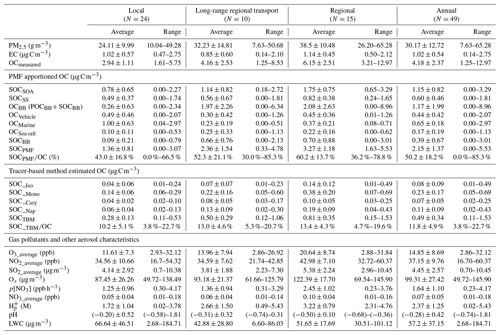
The gas pollutants, i.e., O3, NO2, Ox, and SO2, showed significantly higher average concentrations on regional days than those on LRT local days (Table 2). The annual mean concentrations of O3, NO2, and SO2 were 14.85 ± 8.69 ppb, 37.15 ± 9.76 ppb, and 4.45 ± 2.57 µg m−3, respectively. Given that O3 and NO2 undergo a rapid photochemical conversion in the ambient atmosphere, the tropospheric odd oxygen Ox (the sum of O3 and NO2) was calculated as an indicator of atmospheric oxidation capacity. As shown in Table 1, Ox ranged from 49.72 to 145.90 µg m−3, with a mean value of 99.31 ± 27.42 µg m−3, indicating a high oxidation capacity of the Hong Kong atmosphere. The annual average concentrations of OC and EC were 4.18 ± 2.37 and 1.02 ± 0.54 µg C m−3, respectively. Ambient OC levels observed on regional days (6.15 ± 2.51 µg C m−3) were about 2 times higher than those on LRT and local days; as for EC, it exhibited relative constant levels throughout the year (0.14–2.75 µg C m−3). This confirms that EC is mainly emitted locally in Hong Kong, and OC has some regional sources. Moreover, the OC/EC ratios of the collected samples ranged from 1.51 to 10.91, with an annual average value of 4.61, indicating that secondary formation could be a dominant source of OA in this region (Mancilla et al., 2015). Our previous study has observed that SOC contributed 45 % to OC in Hong Kong during the summer of 2006 (Hu et al., 2010). Here the analysis was expanded to samples taken during the 1-year period to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of sources and their contributions to ambient OA in Hong Kong and the factors that impact ambient SOA formation.
3.1 Characterization of SOA tracers and other polar oxygenated organic compounds
The concentration levels of 39 organic species, including 14 SOA tracers, 12 saccharides, 11 di- and tricarboxylic acids, 4-nitrocatechol, and cholesterol, under different meteorological conditions, are listed in Table 1.
3.1.1 SOA tracers of isoprene, monoterpenes, β-caryophyllene, and naphthalene
Seven isoprene SOA (Isop_SOA) tracers, i.e., 2-methylglyceric acid, two methyltetrol isomers (2-methylthreitol and 2-methylerythritol), three C5-alkene triol isomers (cis-2-methyl-1,3,4-trihydroxy-1-butene, 3-methyl-2,3,4-trihydroxy-1-butene, and trans-2-methyl-1,3,4-trihydroxy-1-butene), and 3-MeTHF-3,4-diols (including both cis- and trans-3-methyltetrahydrofuran-3,4-diols) were identified and quantified. The sum of all Isop_SOA tracers ranged from 1.67 to 117.17 ng m−3, with the annual mean value of 22.78 ± 26.06 ng m−3. Among the Isop_SOA tracers, methyltetrols and C5-alkene triols were the most abundant, and they are suggested to be formed through the acid-catalyzed ring-opening reactions of isoprene epoxydiols (IEPOXs) under low-NOx condition (Chan et al., 2010; Surratt et al., 2010). Higher concentrations of Isop_SOA tracers were measured in summer and autumn than in winter and spring. This could be caused by the higher temperature, stronger solar radiation, and higher emission of isoprene in summer and autumn than in the other two seasons, which promoted the SOA formation from isoprene. This seasonal pattern is consistent with what was observed in other studies (Ding et al., 2012; Kleindienst et al., 2007; Lewandowski et al., 2008). However, if we compare the levels of isoprene tracers monitored at different sites during summer, the total amount of Isop_SOA tracers measured in Hong Kong was about 5 times lower than those measured in several cities in the USA and a rural site (Wangqingsha (WQS) site) in the PRD area (Ding et al., 2012; Kleindienst et al., 2007; Lewandowski et al., 2008). This may be due to the different levels of isoprene, OH radical, and NOx at these sampling sites. The 3-MeTHF-3,4-diols, tracers formed through the intermolecular rearrangement of IEPOX under acidic conditions, was identified in Hong Kong PM2.5 samples for the first time. It has an annual mean concentration of 0.23 ± 0.10 ng m−3, which was about 70 times lower than that in Birmingham, USA (Rattanavaraha et al., 2016), but was comparable to what was observed at the WQS site in the PRD area (Q. F. He et al., 2018). 2-Methylglyceric acid, an isoprene tracer formed from methacrylic acid epoxide (MAE) and hydroxymethyl-methyl-α-lactone (HMML) under high-NOx conditions (Lin et al., 2013; Nguyen et al., 2015), presented a quite different temporal trend from those of the other six Isop_SOA tracers, with the highest concentration in winter and then autumn, summer, and spring. Chamber studies suggested that MAE is an oxidation product resulting from the OH addition to methacryloyl peroxynitrate (MPAN), and its production is temperature dependent (Roberts and Bertman, 1992; Worton et al., 2013). Under higher temperatures, the loss of MPAN is dominated by thermal decomposition, which does not produce SOA tracers through the NO/NO2 pathway. Under lower temperatures, thermal decomposition of MPAN is limited, and more MPAN reacts with OH to generate MAE. Therefore, the lower temperatures in winter would favor the production of MAE and the MAE Isop_SOA tracers, such as 2-methylglyceric acid. Moreover, all Isop_SOA tracers exhibited higher concentrations on regional days than LRT and local days. On regional days, air masses transported from the PRD area worsened the air quality in Hong Kong, and the higher levels of gaseous pollutants, e.g., O3, NO2, Ox, and SO2 (Table 2), promoted SOA formation.
Generally speaking, at an urban location with anthropogenic NOx emissions from automobiles and power plants, the generation of Isop_SOA tracers from the MAE NO/NO2 pathway should be more favored than the IEPOX HO2 channel. However, in this study, 94 % of the total mass of the quantified Isop_SOA tracers was produced through the IEPOX HO2 pathway. A similar phenomenon was observed at the WQS site in the PRD region (Q. F. He et al., 2018). Therefore, to better understand the influences of environmental factors on isoprene SOA formation in the region, we applied the kinetic models described by Eddingsaas et al. (2010), Worton et al. (2013), and Birdsall et al. (2014) to investigate the fate of both IEPOX and MAE in the atmosphere. Besides their degradation through acid-catalyzed ring-opening reactions on particles, IEPOX and MAE can also be oxidized in the gas phase or removed by dry deposition (Eddingsaas et al., 2010). We applied the Kintecus kinetic model (Ianni, 2015) to quantitatively evaluate the fractions of these two Isop_SOA intermediates that undergo gas-phase oxidation, aerosol-phase acid-catalyzed ring-opening reaction, and dry deposition processes. Details of the model calculations are provided in the appendices.
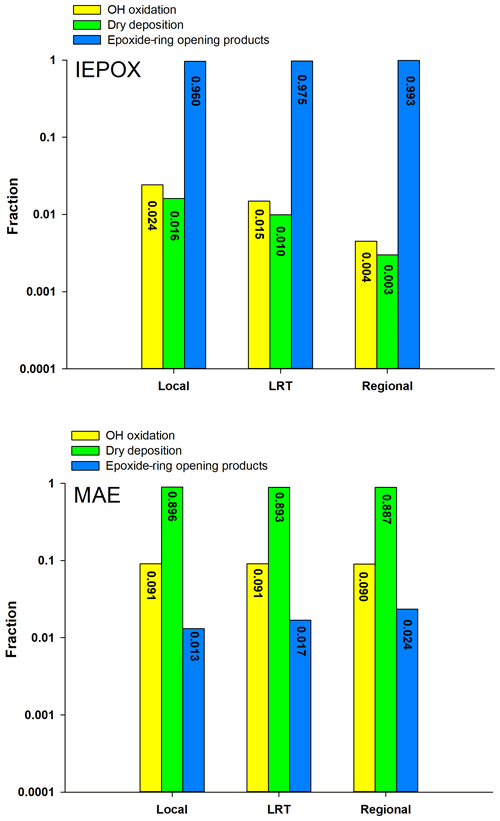
Figure 1Comparison of three degradation processes for IEPOX and MAE under the three synoptic conditions.
Figure 1 shows the comparison of the three elimination processes of IEPOX and MAE during the sampling period in Hong Kong. Given the high volatility of MAE (vapor pressure: atm) (Worton et al., 2013), it has a low tendency to partition into the particle phase and its uptake onto aqueous particles is mainly governed by Henry's law constant (). Worton et al. (2013) estimated the value of MAE to be 7.5×106 M atm−1, which is 20 times lower than that of IEPOX (1.3×108 M atm−1). Moreover, Riedel et al. (2015) suggested that the heterogeneous reactive uptake coefficient of MAE () through the ring-opening reaction was a factor of 30 lower than that of IEPOX. Therefore, as shown in Fig. 1, MAE was primarily eliminated by dry deposition (>80 %) in the gas phase, and only a trivial fraction was degraded through the ring-opening reactions (≤2 %). Our results on the fate of MAE were similar to those observed at the University of California Blodgett Forest Research Station (UC-BFRS) (Worton et al., 2013). However, our results on the relative contributions of these three degradation pathways to IEPOX loss were quite different from theirs, indicating a more sensitive response of IEPOX than MAE to the change of environmental oxidants and conditions. Given the high liquid water content (LWC; mean: 57.20 ± 37.15 µg m−3) and particle acidity (H; mean: −0.28 ± 0.42) of PM2.5 samples in this study (Table 2), the particle-phase ring-opening reaction (Frop) was the dominant degradation pathway of IEPOX in the Hong Kong atmosphere (average: 97.6 %), and its loss through dry deposition and gas-phase oxidation is almost negligible. The Frop of IEPOX reported by Worton et al. (2013) was only 0.02 %, mainly due to the much lower LWC (mean: 0.4 µg m−3) and weaker H (pH mean: 4.4) of their PM2.5 samples. These results demonstrated that particle-phase LWC and H played a more significant role in the atmospheric degradation of IEPOX than MAE. Results from the kinetic model simulation were strongly supported by the experimental finding of IEPOX tracers as the dominant Isop_SOA tracers measured in Hong Kong. The average ratio of IEPOX tracers to MAE tracers was 16.54 (ranged from 3.00 to 71.58), and the average value of was 191.92, confirming that the IEPOX HO2 channel is the major formation pathway of isoprene SOA in the region.
Five SOA tracers of monoterpenes (Mono_SOA), i.e., 3-hydroxyglutaric acid, 3-hydroxy-4,4-dimethylglutaric acid, 3-methyl-1,2,3-butanetricarboxylic acid, 3-isopropylpentanedioic acid, and 3-acetyl pentanedioic acid, were identified and quantified. Their summed concentrations ranged from 2.54 to 32.57 ng m−3, with an annual average value of 10.76 ± 8.04 ng m−3, which is comparable to that reported at the WQS site in the PRD region but lower than that measured in the USA (Ding et al., 2012; Kleindienst et al., 2007; Lewandowski et al., 2008). All Mono_SOA tracers showed the highest level on regional days (mean: 18.00 ± 9.28 ng m−3), followed by LRT (mean: 10.31 ± 7.33 ng m−3) and local days (mean: 6.41 ± 2.75 ng m−3) (Table 1). Although a higher emission and faster photochemical degradation of monoterpenes are expected in summer due to the intense solar radiation and high temperature, higher levels of Mono_SOA tracers were monitored in autumn and winter than in the other two seasons, similar to what was observed at the WQS site (Ding et al., 2014). This seasonal trend of monoterpene SOA tracers may be partly due to the lower mixing height and temperature during autumn and winter, which favored the partition of Mono_SOA tracers into the aerosol phase. Moreover, most of the regional days were identified in autumn and winter. The higher levels of NOx, O3, Ox, and SO2 on regional days (Table 2) are also responsible for the enhanced monoterpene SOA production in autumn and winter. Among Mono_SOA tracers, 3-hydroxyglutaric acid (3HGA) was the most abundant, contributing ∼60 % to the total mass of Mono SOA tracers. Smog chamber experiments showed that the production yield of 3-methyl-1,2,3-butanetricarboxylic acid (MBTCA) from α-pinene/NOx oxidation was significantly higher than those from the β-pinene/NOx and d-limonene/NOx experiments (Jaoui et al., 2005). Therefore, the ratio of 3HGA MBTCA was used as a criterion to differentiate SOA from α-pinene and other monoterpenes (Ding et al., 2014). The value of this ratio was obviously higher on regional days (8.58 ± 2.69) than those on LRT (6.64 ± 3.63) and local days (5.62 ± 3.14), indicating that monoterpenes other than α-pinene, such as β-pinene and d-limonene, might have a more significant contribution to SOA on regional days in the region.
β-Caryophyllinic acid is the SOA (Cary_SOA) tracer of β-caryophyllene, and it ranged from 0.49 to 5.82 ng m−3, with an average annual mean value of 1.53 ± 1.07 ng m−3. Similar to the other SOA tracers, β-caryophyllinic acid showed the highest concentrations on regional days (mean: 2.33 ± 1.21 ng m−3) than LRT (1.73 ± 1.16 ng m−3) and local days (0.94 ± 0.41 ng m−3) (Table 1). For its seasonal trend, β-caryophyllinic acid also exhibited the highest concentration in autumn and winter than the other two seasons. The SOA tracer of toluene, 2,3-dihydroxy-4-oxopentanoid acid, was undetectable in this study, mainly due to its trace level in the Hong Kong atmosphere (Hu et al., 2008) and the limited sensitivity of GC with quadrapole MS. Even in our previous study on a batch of summer PM2.5 samples using a more sensitive GC with ion trap MS, it was barely quantified with a concentration of less than 1 ng m−3 in most samples (Hu et al., 2008). Phthalic acid was suggested as the SOA tracer of naphthalene, given its abundance in both naphthalene SOA and ambient OA (Kleindienst et al., 2012). With the awareness of the potential uncertainties, e.g., the primary origin of phthalic acid from biomass burning, we adopted phthalic acid as the SOA tracer of naphthalene representing the SOA formation from anthropogenic VOCs. The concentration levels of phthalic acid ranged from 0.80 to 16.42 ng m−3, with an average of 4.31 ± 3.39 ng m−3. Similar to the other SOA tracers, it also showed the highest concentrations on regional days (7.16 ± 3.61 ng m−3) than LRT (4.97 ± 3.30 ng m−3) and local days (2.26 ± 1.38 ng m−3) (Table 1).
3.1.2 Saccharides and dicarboxylic acids
Twelve saccharides, i.e., levoglucosan, arabitol, fructose, meso-erythritol, sucrose, galactosan, mannitol, sorbitol, galactose, glucose, xylose, and xylitol, have been quantified. Of the 12 saccharides, levoglucosan, a tracer of BB, was by far the most abundant (range: 0.64–474.15 ng m−3; mean: 75.02 ± 111.43 ng m−3). It showed the highest levels on regional days (about 6 times higher than that on local days), especially during winter when BB activities in the PRD region were most frequent. Two primary saccharides, i.e., fructose and xylose, also exhibited the highest levels on regional days. They showed good correlations with levoglucosan (R2=0.65 and 0.93), suggesting that they could be from BB as well.
Among the identified dicarboxylic acids, oxalic acid was the most abundant, followed by terephthalic acid, phthalic acid, malic acid, succinic acid, and others. Most dicarboxylic acids, including the five most abundant ones, showed higher levels on regional days; they were found with higher levels in winter and autumn as well. This temporal trend is similar to what we have observed for Mono_SOA tracers and most saccharides, indicating that regional pollution had a dominant influence on the abundance of both primary and secondary aerosols in Hong Kong, far exceeding the influence of other environmental parameters, such as temperature and solar radiation. Atmospheric dicarboxylic acids have various sources. For example, oxalic acid was suggested to be secondarily formed from biogenic emissions and anthropogenic sources (e.g., BB and automobile exhaust) through both gas-phase reactions and in-cloud processing (Yu et al., 2005). Malic acid was suggested to be the photo-degradation product of both succinic acid and biogenic SOA compounds (Hu and Yu, 2013). In this study, malic acid was found to be strongly correlated with 3HGA (R2=0.96) and ΣMono_SOA tracers (R2=0.95) throughout the year, providing more evidence to the hypothesis that malic acid is a late-stage oxidation product of BVOCs, especially monoterpenes (Hu and Yu, 2013). Ambient terephthalic acid was mainly directly emitted from plastic waste incineration (Simoneit et al., 2005) and was used as a marker of waste incineration.
Besides dicarboxylic acids, two benzenetricarboxylic acids (i.e., 1,2,3- and 1,2,4-benzenetricarboxylic acids), 4-nitrocatechol, and cholesterol were also quantified. The two benzenetricarboxylic acids were suggested to be the photo-degradation products of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) emitted from combustion activities (Kautzman et al., 2010). We have previously identified them in the water-soluble humic-like substance (HULIS) extracts of PM2.5 samples collected in Beijing and Hong Kong (Ma et al., 2018, 2019). The annual mean concentrations of 1,2,3- and 1,2,4-benzenetricarboxylic acids measured in this study were 2.27 ± 1.97 ng m−3 (range: 0.47–9.50 ng m−3) and 3.13 ± 2.68 ng m−3 (0.47–12.54 ng m−3), respectively, which were comparable to what was measured at the other four sites in the PRD region (X. He et al., 2018). The 4-nitrocatechol, which was secondarily generated from the photo-oxidation of naphthalene, was suggested as a tracer of atmospheric aging of a BB plume (Kitanovski et al., 2012). It strongly correlated with levoglucosan (R2=0.88) and exhibited higher levels on regional days and during winter, which further confirmed its BB origin in the region. Therefore, the two benzenetricarboxylic acids and 4-nitrocatechol were included in PMF analysis as the SOA tracers of BB aging.
3.2 Source apportionment of organic aerosols
In this study, the US EPA PMF 5.0 was used to determine the major OA sources and to quantify their contributions to OC. Eighteen species were input into PMF, including EC, OC, Ni, V, major ions, and various primary and secondary organic tracers. Given their similar origins, some organic tracers were lumped together, and the lumped species were used as the fitting species in PMF. They were (1) C5-alkene triols, which is the sum of the three C5-alkene triol isomers; (2) IsopT, which is the sum of two methyltetrol isomers and 2-methyl glyceric acid; (3) MonoT, which is the sum of the five monoterpenes SOA tracers; and (4) Hopane, which is the sum of the four hopanes. Since C5-alkene triols were not in the SOA tracers list of the TBM (Kleindienst et al., 2007), the lumped C5-alkene triols were used as a separated fitting species in PMF. PMF solutions were tested with four to eight factors. A hundred base runs were performed in each modeling run, and the run with the minimum Q value was selected. The uncertainty values of each input species were calculated using the method described in our previous studies (Hu et al., 2010; Ma et al., 2016), which were set to be 20 % of the mean concentrations for OC and EC and 40 % of mean values for cations, anions, and all organic species. An extra modeling uncertainty of 10 % was used to account for possible temporal changes in the source profiles. The ratio was 1.00, and scaled residuals were normally distributed between −0.2 and 0.2, indicating no influence of outliers on the solution. A hundred bootstrap runs were performed with a minimum correlation R value to examine the base run solution's stability and uncertainty. All bootstrapped factors were explicitly mapped to factors identified in base solution with no exception. In the displacement (DISP) assessment, no error was found, and the drop in Q value was less than 1 %, suggesting a stable solution. No swap factor appeared at dQmax=4, indicating there was no considerable rotational ambiguity in the solution. Rotations were introduced to the solutions by adjusting the “FPEAK” value from −1 to +1, and the non-rotated solutions (FPEAK = 0.0) were considered to be the most interpretable ones. Moreover, a strong linear correlation between the measured and PMF-predicted OC (OCPMF) (R2=0.92) was observed, which also suggested a reliable PMF solution.
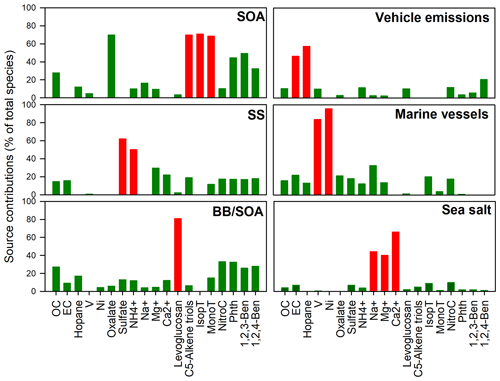
Figure 2PMF-apportioned source contributions (% of total species) to ambient PM2.5 samples collected in Hong Kong. Red column: chemical markers for source identification.
As shown in Fig. 2, the first factor was distinguished by high loadings of oxalate and biogenic SOA tracers, suggesting the secondary origin of this source. The second factor was dominated by large amounts of SO and NH, suggesting the process of secondary sulfate formation. In the third factor, about 90 % of levoglucosan was portioned into it, accompanied by 4-nitrocatechol, phthalic acid, and the two benzenetricarboxylic acids, indicating both the primary emission and aging of BB plume. Therefore, this factor was defined as BB and SOA (BB/SOA). The fourth factor was identified as vehicular emissions due to the large amounts of hopanes and EC portioned in this factor. The fifth factor has large amounts of Ni and V, which are signatures of residual oil combustion from the marine vessel class (Viana et al., 2009). It is well known that Hong Kong is one of the busiest container ports globally, which handles 50 % of the PRD's total cargo throughput. Therefore, the fifth factor was identified as marine vessels. The sixth factor has a high loading of Na+, Mg2+, and Ca2+, indicating the sea salt source.
The amount of OC apportioned to each factor in PMF analysis was considered the contribution of that source to ambient OC. Therefore, the two leading sources contributing to ambient OC in Hong Kong were BB (including both primary emission and aging process, OCBB: 27.9 %, 1.17 ± 1.99 µg C m−3) and SOA (SOCSOA: 27.5 %, 1.15 ± 0.82 µg C m−3), followed by marine vessels (OCmarine: 15.6 %, 0.65 ± 0.58 µg C m−3), secondary sulfate (SS) (SOCSS: 14.5 %, 0.60 ± 0.46 µg C m−3), vehicle emissions (OCvehicle: 10.5 %, 0.44 ± 0.42 µg C m−3), and sea salt (OCsea: 4.0 %, 0.17 ± 0.19 µg C m−3) (Table 2 and Fig. 3). Since a fraction of SOA from the aging of BB (SOCBB) was apportioned into the BB/SOA factor, we calculated SOCBB using the following equation:
where OCBB and [LEVOBB] are the amounts of OC and levoglucosan portioned in the BB/SOA factor, respectively. Using levoglucosan as the tracer of primarily emitted BB OA, we calculated the amounts of primary organic carbon (POC) from BB (POCBB) by dividing [LEVO]BB with 0.082, where 0.082 is the average ratio of levoglucosan to POC from the burning of major types of Chinese cereal straws (i.e., rice, wheat, and corn) obtained in combustion chamber experiments (Zhang et al., 2007). As cereal straws are one of the most common BB fuels in China, the above ratio (0.082) has been used to estimate BB contribution to POC in both Beijing (Zhang et al., 2008) and Hong Kong (Sang et al., 2011). Therefore, it was adopted to calculate POCBB in this study.
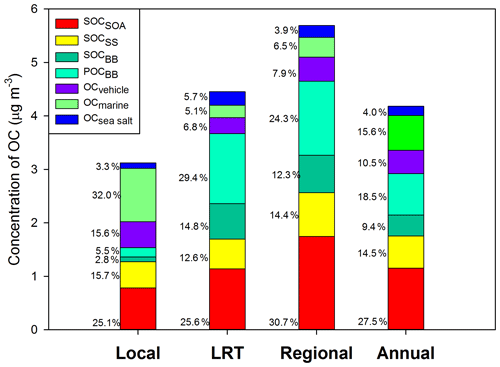
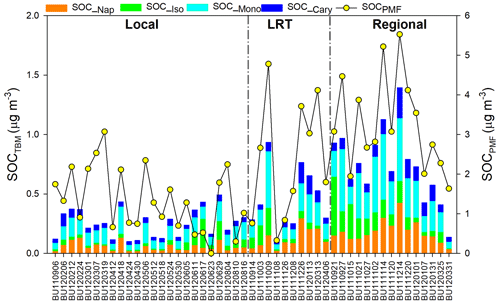
Figure 3Source-specific contributions to OC under different meteorological conditions. OCBB was split into POCBB and SOCBB.
Based on PMF results, the source-specific contributions to OC are presented in Table 2 and demonstrated in Fig. 3. The total SOC apportioned by PMF (SOCPMF), i.e., the sum of SOCSOA, SOCSS, and SOCBB, accounted for 51.4 % (2.15 ± 1.37 µg C m−3) of OC in Hong Kong, with the secondary organic-rich sources (i.e., SOCSOA+ SOCBB) contributing 36.9 % (1.54 ± 1.13 µg C m−3) to total OC. Huang et al. (2014) also reported that secondary organic-rich sources accounted for 30 %–40 % of OC in Guangzhou, which is another PRD site. A higher level of SOCPMF and its contribution to OC were observed on regional days (3.27 ± 1.18 µg C m−3, 57.4 %) compared to LRT (2.36 ± 1.54 µg C m−3, 53.0 %) and local days (1.36 ± 0.81 µg C m−3, 43.6 %). An even starker difference in the amounts of SOCBB between regional and local days was observed, which was 8 times higher on the regional days. This suggested that nonlocal sources were the dominant contributors to SOCBB. BB activities were intensive in the PRD region, especially during fall and winter. On regional days, freshly emitted and aged gaseous and aerosol-phase pollutants from the open burning of rice straws and other crops were transported from the northern PRD region into Hong Kong (Hu et al., 2010). Huang et al. (2014) examined the aging of BB plume at low temperatures. They found that the production of BB SOA was rapid at a typical OH radical concentration of wintertime China, and the amount of BB SOA may exceed BB POA in 4–14 h even at −10 ∘C. Given that the average temperatures in Hong Kong during autumn and winter were 26.15 and 17.76 ∘C, respectively; the formation of BB SOA should be achieved even quicker during the regional transport. As expected, SOCSOA also showed a higher average concentration on regional days (1.75 ± 0.75 µg C m−3) than on LRT (1.14 ± 0.82 µg C m−3) and local days (0.78 ± 0.65 µg C m−3), which is consistent with the trends of all SOA tracers. Although SOC from secondary inorganic-rich sources (SOCSS) exhibited the highest levels (0.82 ± 0.38 µg C m−3) on regional days as well, its contribution to OC was relatively stable under the three synoptic conditions (Fig. 3). Several studies showed that SO2 transported from the northern PRD region promoted secondary sulfate formation in Hong Kong through both gas-phase and in-cloud oxidation pathways (Lu and Fung, 2016; Yu et al., 2005; Yuan et al., 2006). A recent study proposed that the sulfate formation in aqueous aerosols through NO2 oxidation and ammonium neutralization can simultaneously enhance the production of both nitrate and SOA (Wang et al., 2016), which helps explain the considerable amount of SOCSS apportioned.
OC from the four primary sources, i.e., POCBB, OCmarine, OCvehicle, and OCsea, accounted for 48.6 % of total OC throughout the year. Similar to SOCBB, POCBB showed a higher level (1.38 ± 1.75 µg C m−3) on regional days due to a large number of emissions from BB activities in the northern PRD area. OCvehicle remained a higher contribution on local days (15.6 %, 0.49 ± 0.46 µg C m−3), consistent with our previous finding that vehicle emission is a local pollution source (Hu et al., 2010). Similarly, marine vessels accounted for a greater amount and larger fraction of OC on local days (32.0 %, 1.00 ± 0.63 µg C m−3) than LRT (5.2 %, 0.23 ± 0.19 µg C m−3) and regional days (6.5 %, 0.37 ± 0.21 µg C m−3). On local days, the southeastern to southwestern wind brought pollutants from residual oil combustion from the ocean into Hong Kong, leading to a higher OCmarine.
In summary, both secondary aerosol sources and air mass origins play important roles in atmospheric OC in Hong Kong. On regional days, air mass transported from the northern PRD area brought large amounts of air pollutants into Hong Kong, which promoted the SOA production from both anthropogenic emissions and BVOCs and resulted in a fraction of 57.4 % of OC being secondarily formed. On the other hand, local sources, including vehicle emissions and marine vessels, became more critical and significantly contributed to OC (56.4 %) on local days.
3.3 Estimation of SOC origin
To better understand the SOA precursors and their contributions to SOA/SOC in the region, we adopted a tracer-based method (Kleindienst et al., 2007, 2012; Offenberg et al., 2007) to estimate the SOA/SOC formation from a group of selected biogenic and anthropogenic hydrocarbons, i.e., isoprene, monoterpenes, β-caryophyllene, and naphthalene. The mass ratio of tracer compounds to the total SOC (fSOC) generated from individual VOC precursors was derived from smog chamber experiments (Kleindienst et al., 2007; Offenberg et al., 2007). By assuming the same fSOC value of the precursor under smog chamber conditions and in ambient air, one can use the quantified SOA tracer concentrations to estimate the amount of SOC from that precursor in the real atmosphere. It has been well noted that results obtained from this tracer-based method are subject to potential uncertainties from various aspects, e.g., the larger variation of precursor concentrations and more complicated environmental conditions in the real atmosphere than in smog chamber experiments; the decay of some tracer compounds during transport; mismatch of ambient and smog-chamber-generated SOA compositions, using surrogates other than ketopinic acid for the quantification of tracer compounds; and so on (Ding et al., 2014; Hu et al., 2008; Kleindienst et al., 2012, 2007). However, using the tracer-based method, we can at least have a rough estimation of the key SOA precursors in the region, their contributions to ambient OC, and the amount of SOC from unknown precursors. Wang et al. (2013) noted that the SOA tracer-based method would significantly underestimate SOC_Mono in the PRD region. Ding et al. (2014) gave a reasonable explanation that the mismatch of monoterpene tracers measured in ambient air and used to derive fSOC of monoterpenes in chamber studies may increase the uncertainty of SOC_Mono. Thus, they picked the five Mono_SOA tracers measured in their samples and derived the fSOC and fSOA values using the SOA tracers data and SOA/SOC concentrations reported by Offenberg et al. (2007). In this study, we only measured five out of nine monoterpene SOA tracers in Offenberg et al. (2007). Similar to Ding et al. (2014), to lower the uncertainty induced from the mismatch of SOA tracer compositions, we derived a fSOC_mono value of 0.047 based on the experimental data by Offenberg et al. (2007) and applied it to estimate SOC_Mono. Many research groups have adopted this tracer-based method to assess SOC productions from the five studied VOCs at various locations in the world, and reasonable results have been obtained (Ding et al., 2012; Fu et al., 2014; Hu et al., 2008; Hu and Yu, 2013; Kleindienst et al., 2012, 2007; Lewandowski et al., 2008).
As shown in Table 2, SOC estimated by the tracer-based method (SOCTBM) ranged from 0.11 to 1.53 µg C m−3 in Hong Kong, accounting for 3.8 % to 22.7 % of ambient OC levels. It exhibited the same trend as OC and SOCPMF (Fig. 4), i.e., with higher concentrations on regional days (0.81 ± 0.35 µg C m−3) than on LRT (0.50 ± 0.29 µg C m−3) and local days (0.28 ± 0.13 µg C m−3). Similar to our previous study, monoterpenes were found to be the most significant SOC contributor in the region, with SOC_Mono ranging from 0.05 to 0.69 µg C m−3 and having an average concentration of 0.23 ± 0.17 µg C m−3. SOC_Iso and SOC_Cary, on the other hand, were about 3 times smaller than SOC_Mono and were 0.08 ± 0.09 and 0.07 ± 0.05 µg C m−3, respectively. Smog chamber experiments have been carried out to study the SOA yields from •OH oxidation, ozonolysis, and nitrate radical (NO3) oxidation of monoterpenes and isoprene, and monoterpenes were found to be more effective in SOA production than isoprene (Lee et al., 2006a, b). Highly oxygenated organic molecules with low and extremely low volatilities were formed from the oxidation of monoterpenes and observed in both laboratory experiments and field measurements (Ehn et al., 2014; Jokinen et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2018). Moreover, a synergistic O3+OH oxidation pathway of monoterpenes was recently proposed, which leads to the formation of extremely low-volatility oligomers and may result in even larger monoterpene SOA yields in the real atmosphere than what observed in the smog chamber experiments (Kenseth et al., 2018). Tsui et al. (2009) reported a total BVOC emission of 8.6×109 g C yr−1 in Hong Kong, with 40 % from monoterpenes and 30 % from isoprene. The remaining 30 % could be sesquiterpenes (e.g., β-caryophyllene) or other BVOCs. Therefore, the predominance of monoterpenes SOA in BVOCs-derived SOC is likely due to the combined effects of their high SOA yields and large emissions in the region. Like the SOA tracers, SOC from the four precursors all showed the highest level on regional days than those on LRT and local days (Table 2). On regional days, large amounts of VOC precursors and gaseous oxidants could be brought into Hong Kong through the regional transport of air masses from northern PRD and oxidized along the way. Conversely, on local days, the ocean breeze brings clean air masses from the South China Sea into Hong Kong, leading to a dilution effect of local air pollution. These results highlight that air mass origins play an important role in the SOC formation from both biogenic and anthropogenic VOCs. Given that SOCTBM is calculated based on the concentration levels of individual SOA tracers measured in the ambient aerosols, it is reasonable that SOC attributed to each VOC precursor showed the same meteorological variations as their SOA tracers.
We observed similar temporal trends between SOCPMF and SOCTBM (R2=0.71). However, SOCTBM only accounted for 26.5 % of SOCPMF, suggesting SOC must have been underestimated by the tracer-based method. A reasonable explanation is that secondary formation from nighttime reactions, multiphase reactions, and other SOA precursors are not considered in the SOA tracer-based method. Parameters used in the tracer-based method were derived from pure gas-phase photo-oxidation of VOC precursors in smog chambers (Kleindienst et al., 2007, 2009). Therefore, it is better to be used as a complementary method with PMF in the source apportionment study of ambient OC, especially SOC.
3.4 Effects of anthropogenic influences on secondary aerosol formation
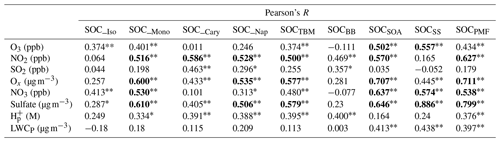
Increasing evidence from laboratory studies and ambient observations has shown that anthropogenic emissions can significantly affect SOA formation from terpenoids through multiple chemical processes in both daytime and nighttime (Xu et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2018). We conducted the Pearson's R correlation analysis of all SOC terms (i.e., SOC_Iso, SOC_Mono, SOC_Cary, SOC_Nap, SOCTBM, SOCPMF, SOCBB, SOCSOA, and SOCSS) with O3, NO2, SO2, Ox, NO3, sulfate, particle acidity (H), and particle liquid water content (LWCP) (Table 3). Details on the calculation of H and LWCP are presented in Appendix B. Since NO3 was not directly monitored at HKEPD stations, its mixing ratio was estimated using the following equation:
The numerator is the production of NO3 (p[NO3]) from O3 and NO2, and the denominator is the reactivity of NO3 for NO3–VOC reactions. From the IUPAC database, we obtained the temperature-dependent expression of k1 (cm3 molecules−1 s−1, the production rate constant of NO3) as exp(), where T is the ambient temperature in kelvin. Therefore, using k1 and the measured concentration levels of [O3] and [NO2], we calculated p[NO3] (Table 2). Brown et al. (2016) reported a NO3–VOC reactivity of s−1 in Hong Kong with a corresponding NO3 lifetime of 2.5 min. NO3 was then calculated as the ratio of p[NO3] to this NO3 reactivity value, and an annual mean level of 70 ± 47 ppt was estimated.
As we mentioned earlier, Ox is an indicator of atmospheric oxidation capacity. Five SOC terms, i.e., SOC_Mono, SOC_Nap, SOCTBM, SOCSOA, and SOCPMF, showed significant positive correlations with Ox, especially SOCSOA and SOCPMF (R>0.7, P<0.01). However, only SOCSOA and SOCSS were found to be significantly correlated with O3 (R>0.50, P<0.01). As for NO2, another critical component of Ox, it exhibited statistically significant positive correlations with not only SOCSOA and SOCPMF but also several TBM estimated SOCs, including SOCTBM, SOC_Mono, SOC_Nap, and SOC_Cary. This may be because SOA tracers used in TBM were produced from the photo-oxidation of these VOC precursors in the presence of NOx (Kleindienst et al., 2007). The significant positive correlations between NO2 and SOCSOA and SOCPMF also suggest that the daytime oxidation processes involving NOx are critical SOA formation pathways in the region. Significant correlations with R>0.5 between NO3 and SOC_Mono, SOCSOA, SOCPMF, and SOCSS were also observed. BVOCs were found to account for >80 % of the NO3 reactivity in Hong Kong (Brown et al., 2016), with monoterpenes as the leading contributor. Both Zhang et al. (2018) and Xu et al. (2013) have reported an enhancement of nighttime monoterpenes SOA in the southeastern USA by NO3–monoterpene reactions. Therefore, our findings indicate that SOA formation through nighttime NO3 oxidation of biogenic VOCs, especially monoterpenes, may have made a considerable contribution to the SOA loading in Hong Kong. However, more field measurement data, e.g., quantification of the particle-phase organic nitrates using real-time online mass spectrometry techniques, are needed to examine the impact of NOx processing on SOA formation in the region.
Since NO3 is a key precursor of nighttime production of HNO3, and nitrate is a significant component of secondary inorganic aerosols, it rationalized the correlations between NO3 and SOCSS. Six SOC terms, i.e., SOC_Mono, SOC_Nap, SOCTBM, SOCSOA, SOCSS, and SOCPMF, showed significant positive correlations with sulfate, especially SOCSS and SOCPMF (R≥0.8, P<0.01). Given that sulfate is the key component of secondary inorganic aerosol, such a strong correlation between SOCSS and sulfate is expected. Moreover, several studies have suggested that sulfate also plays a dominant role in the production of aerosol-phase organosulfates through both nucleophilic addition reactions and the salting-in effect (Lin et al., 2012; Riva et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2015).
We then performed multivariate linear regression (MLR) analysis to obtain a quantitative and comprehensive understanding of the impacts of gaseous oxidants and aerosol characteristics on SOCTBM, SOCPMF, and the individual PMF-apportioned SOCs (i.e., SOCSS, SOCSOA, and SOC_BB). Six parameters, namely, O3, NO2, NO3, sulfate, H, and LWCP, were included in the preliminary runs. However, the MLR results showed that O3 was an insignificant factor for all SOC terms, even with negative regression coefficients. Pearson's R analysis also showed that SOC was more NO2 dependent than O3. Therefore, it was excluded from the final MLR analysis, and the results are shown in Table 4.
Table 4Results of multivariate linear analysis of PMF and TBM-resolved SOCs, NO2, NO3, sulfate, particle acidity (H), and total particle-phase liquate water content (LWCP). **: P<0.01; *: P<0.05. Note that significant regressions are bold.
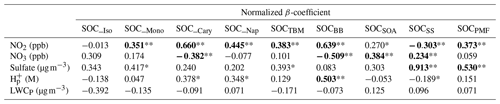
We found that two parameters, i.e., sulfate and NO3, have statistically significant positive linear relationships (P≤0.001) with SOCSS, and the regression coefficients were 0.913 and 0.234, respectively. The result is reasonable and consistent with what was observed from Pearson's R analysis, given that sulfate is the critical component in the PMF identified SS factor, and NO3 is the precursor of nitrate through HNO3 formation at nighttime. As for SOC_BB, three parameters, i.e., NO2, NO3, and H, showed significant linear relationships with it (P<0.01), with a regression coefficient of 0.639, −0.509, and 0.503, respectively. This indicates that a 1 mol L−1 increase in particle acidity was associated with a 0.503 µg C m−3 increase in SOC from BB aging. Phenols, which are produced from the combustion of lignin, are a typical class of gaseous compounds emitted in large amounts from BB (Bruns et al., 2016; Schauer et al., 2001). Recent laboratory studies indicate that phenols can undergo multiphase photochemical reactions in the atmosphere with the formation of nitrophenols and nitrocatechols (Finewax et al., 2018; Yu et al., 2014). Vione et al. (2001) observed the aqueous-phase photonitration of phenols, which was pH dependent with more nitro compounds generated at lower pH. Given the strong particle acidity (pH annual mean: −0.28) observed in the Hong Kong atmosphere, the formation of the 4-nitrocatechol and its analogs may be favored in the BB plume, which enhances SOCBB formation.
Both sulfate and NO2 were found as the statistically significant factors that positively correlated with SOCPMF, with regression coefficients of 0.530 and 0.373, respectively (P<0.001, Table 4). This suggests reducing the sulfate level by 1 µg m−3 and NO2 level by 1 ppb could lower the total PMF-apportioned SOC by 0.530 and 0.373 µg C m−3, respectively. NO2 was also the most significant factor influencing SOCTBM, with a regression coefficient of 0.383 (P<0.001), indicating that a decrease of NO2 by 1 ppb can reduce SOCTBM by 0.383 µg C m−3. As for SOCSOA, we found NO3 as the most significant parameter (P<0.01), and a decrease of 1 ppb NO3 can lead to a reduction of SOCSOA by 0.384 µg C m−3 when holding other covariates unchanged. These results are consistent with what was observed from Pearson's R analysis, indicating the importance of NOx processing on both daytime and nighttime SOA production in the region.
In this study, we identified and quantitatively assessed the contributions of six primary and secondary sources to ambient OC in Hong Kong, and secondary formation was found to be the leading contributor. Anthropogenic emissions, including NO2, Ox, NO3, and sulfate, significantly influenced SOA formation in the region. In particular, NOx processing in both daytime and nighttime has played a critical role. Although the ambient NO2 level has dropped by 33.3 % from 1999 to 2019 (the government of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR), https://www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/202001/20/P2020012000874.htm, last access: 16 June 2021) and sulfate level in PM2.5 was also lowered by about 30 % from 2000 to 2016 (Environmental Protection Department of Hong Kong, 2017), the roadside NO2 level was still high. According to the 20-year air pollutants monitoring data released by HKSAR, the annual average concentrations of roadside NO2 were much higher than the other gaseous pollutants, and they peaked during 2011–2013, which were 122 and 118 µg m−3 in 2011 and 2012, respectively. Although the annual ambient level of roadside NO2 decreased to 80 µg m−3 in 2019, it is still 2 times higher than the annual objective level set by the HKSAR government, indicating a continuous significant impact of NOx on SOA formation in Hong Kong, especially in areas with heavy traffic load. Given that 90 % of the roadside NO2 was from commercial vehicles, such as buses, trucks, minibuses, and so on, our results suggest that more stringent control of NOx emission from commercial vehicles is needed. This will benefit the community by reducing not only the background NOx levels but also the SOA pollution in Hong Kong.
In this study, we use Kintecus (Ianni, 2015), a kinetics simulation software, to investigate the degradation pathways of two isoprene SOA intermediates, i.e., IEPOX and MAE, in the atmosphere. Simulation time was set to be 100 h to ensure the completion of reactions. As described by Eddingsass et al. (2010) and Worton et al. (2013), IEPOX and MAE are removed from the atmosphere mainly through three pathways, namely, the gas-phase photo-oxidation, dry deposition, and aerosol-phase acid-catalyzed ring-opening reaction. Reaction constants that are involved in these three degradation processes are listed below.
-
IEPOX:
-
MAE:
The eight terms, i.e., kOX and , kdd and , and , and and , are the gas-phase oxidation rate constants, dry deposition rate constants, acid-catalyzed ring-opening rate constants, and Henry's law constants of IEPOX and MAE, respectively. Given that the annual average OH radical level in the PRD region was 5×106 molecules cm−3 (Hofzumahaus et al., 2009), kOX and were calculated to be s−1 and s−1, respectively, at 298 K. kdd is estimated by the deposition velocity (dv) and the boundary layer height (blh). Like Eddingsaas et al. (2010) and Worton et al. (2013), we assumed the same deposition velocities for IEPOX and MAE as that for hydrogen peroxide (1–5 cm s−1). With the predicted boundary height in Hong Kong of 1100 m (Xie et al., 2012), kdd and were calculated to be s−1. Given the high volatility of MAE vapor pressure ( atm) (Worton et al., 2013), it has a low tendency to partition into the particle phase, and its uptake onto aqueous particles is mainly governed by Henry's law constant (). Worton et al. (2013) estimated the value of MAE to be 7.5×106 M atm−1, which is 20 times lower than that of IEPOX (1.3×108 M atm−1, Minerath et al., 2008). Moreover, Riedel et al. (2015) suggested that the heterogeneous reactive uptake coefficient of MAE () through the ring-opening reaction was a factor of 30 lower than that of IEPOX. The ring-opening rate constant () for IEPOX and MAE were estimated by Eddingsaas et al. (2010) and Birdsall et al. (2014), which are M−1 s−1 and M−1 s−1, respectively. We then inputted all these parameters into the Kintecus model and estimated the fractions of IEPOX and MAE degraded through the three abovementioned pathways.
A thermodynamic model (E-AIM model II) was applied to estimate the hydrogen ion concentration in air (H) and liquid water content associated with inorganic species (LWCinorg). The liquid water content associated with organic species (LWCorg) was calculated using the following equation:
where korg is an organic hygroscopicity parameter and has a value of 0.1, morg is organic mass concentration, and a factor of 2.1 was applied to convert OC to organic matter (OM) at the urban location. ρw is the water density, and a typical value of 1.4 g cm−1 was applied for organic aerosols (ρorg). Since LWC is associated with both inorganic and organic species, the total particle water (LWCp) was calculated as the sum of LWCinorg and LWCorg based on the assumption that particles were internally well mixed.
Particle acidity was calculated using the following equation:
where (mol L−1) is the concentration of hydrogen ions in aerosol water, interpreted as particle acidity. and LWCinorg were calculated by E-AIM model II using input values of inorganic ions, RH, and temperature.
Raw data used in this study are archived at Hong Kong Baptist University and are available upon request by contacting the corresponding author.
YC and DH designed the study. YC did all the experiments and most of the data analysis. YM helped with regression analysis and data interpretation. YC drafted the article. DH helped with data analysis and interpretation and revised the article.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
The authors thank the Environmental Central Facility (ENVF) in The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) for real-time environmental and air quality data (http://envf.ust.hk/dataview/gts/current/, last access: 16 June 2021).
This research has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 21976151 and 21477102) and the Research Grants Council, the University Grants Committee of Hong Kong (grant nos. 12328216, 12304215, and 12300914).
This paper was edited by Nga Lee Ng and reviewed by three anonymous referees.
An, Z., Huang, R.J., Zhang, R., Tie, X., Li, G., Cao, J., Zhou, W., Shi, Z., Han, Y., Gu, Z., and Ji, Y.: Severe haze in northern China: A synergy of anthropogenic emissions and atmospheric processes, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 116, 8657–8666, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1900125116, 2019.
Birdsall, A. W., Miner, C. R., Mael, L. E., and Elrod, M. J.: Mechanistic study of secondary organic aerosol components formed from nucleophilic addition reactions of methacrylic acid epoxide, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 14, 12951–12964, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-12951-2014, 2014.
Brown, S. S., Dubé, W. P., Bahreini, R., Middlebrook, A. M., Brock, C. A., Warneke, C., de Gouw, J. A., Washenfelder, R. A., Atlas, E., Peischl, J., Ryerson, T. B., Holloway, J. S., Schwarz, J. P., Spackman, R., Trainer, M., Parrish, D. D., Fehshenfeld, F. C., and Ravishankara, A. R.: Biogenic VOC oxidation and organic aerosol formation in an urban nocturnal boundary layer: aircraft vertical profiles in Houston, TX, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13, 11317–11337, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-11317-2013, 2013.
Brown, S. S., Dubé, W. P., Tham, Y. J., Zha, Q. Z., Xue, L. K., Poon, S., Wang, Z., Blake, D. R., Tsui, W., Parrish, D. D., and Wang, T.: Nighttime chemistry at a high altitude site above Hong Kong, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 121, 2457–2475, https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD024566, 2016.
Bruns, E. A., El Haddad, I., Slowik, J. G., Kilic, D., Klein, F., Baltensperger, U., and Prévôt, A. S. H.: Identification of significant precursor gases of secondary organic aerosols from residential wood combustion, Sci. Rep.-UK, 6, 27881, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27881, 2016.
Chan, M. N., Surratt, J. D., Claeys, M., Edgerton, E. S., Tanner, R. L., Shaw, S. L., Zheng, M., Knipping, E. M., Eddingsaas, N. C., Wennberg, P. O., and Seinfeld, J. H.: Characterization and quantification of isoprene-derived epoxydiols in ambient aerosol in the southeastern united states, Environ. Sci. Technol., 44, 4590–459, https://doi.org/10.1021/es100596b, 2010.
Cheng, Y., Ma, Y., Dong, B., Qiu, X., and Hu, D.: Pollutants from primary sources dominate the oxidative potential of water-soluble PM2.5 in Hong Kong in terms of dithiothreitol (DTT) consumption and hydroxyl radical production, J. Hazard. Mater., 405, 124218, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124218, 2021.
Ding, X., Wang, X. M., Gao, B., Fu, X. X., He, Q. F., Zhao, X. Y., Yu, J. Z., and Zheng, M.: Tracer-based estimation of secondary organic carbon in the Pearl River Delta, South China, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 117, D05313, https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JD016596, 2012.
Ding, X., He, Q., Shen, R., Yu, Q., Wang, X., Guenther, D., Dlugokencky, E., Lang, P., Newberger, T., Wolter, S., White, A., Noone, D., Wolfe, D., Schnell, R., Ding, X., He, Q., Shen, R., Yu, Q., and Wang, X.: Spatial distributions of secondary organic aerosols from isoprene, monoterpenes, β-caryophyllene, and aromatics over China during summer, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 119, 11877–11891, https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD021748, 2014.
Eddingsaas, N. C., Vandervelde, D. G., and Wennberg, P. O.: Kinetics and products of the acid-catalyzed ring-opening of atmospherically relevant butyl epoxy alcohols, J. Phys. Chem. A, 114, 8106–8113, https://doi.org/10.1021/jp103907c, 2010.
Ehn, M., Thornton, J. A., Kleist, E., Sipilä, M., Junninen, H., Pullinen, I., Springer, M., Rubach, F., Tillmann, R., Lee, B., Lopez-Hilfiker, F., Andres, S., Acir, I. H., Rissanen, M., Jokinen, T., Schobesberger, S., Kangasluoma, J., Kontkanen, J., Nieminen, T., Kurtén, T., Nielsen, L. B., Jørgensen, S., Kjaergaard, H. G., Canagaratna, M., Maso, M. D., Berndt, T., Petäjä, T., Wahner, A., Kerminen, V. M., Kulmala, M., Worsnop, D. R., Wildt, J., and Mentel, T. F.: A large source of low-volatility secondary organic aerosol, Nature, 506, 476–479, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13032, 2014.
Environmental Protection Department of Hong Kong: Hong Kong emission inventory report, available at: https://www.epd.gov.hk/epd/sc_chi/environmentinhk/air/data/emission_inve.html (last access: 16 June 2021), 2017.
Finewax, Z., De Gouw, J. A., and Ziemann, P. J.: Identification and quantification of 4-nitrocatechol formed from OH and NO3 radical-initiated reactions of catechol in air in the presence of NOx: Implications for secondary organic aerosol formation from biomass burning, Environ. Sci. Technol., 52, 1981–1989, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05864, 2018.
Finlayson-Pitts, B. J. and Pitts, J. N.: Chemistry of the upper and lower atmosphere, Academic Press, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-257060-5.X5000-X, 2000.
Fry, J. L., Kiendler-Scharr, A., Rollins, A. W., Wooldridge, P. J., Brown, S. S., Fuchs, H., Dubé, W., Mensah, A., dal Maso, M., Tillmann, R., Dorn, H.-P., Brauers, T., and Cohen, R. C.: Organic nitrate and secondary organic aerosol yield from NO3 oxidation of β-pinene evaluated using a gas-phase kinetics/aerosol partitioning model, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 1431–1449, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-1431-2009, 2009.
Fu, P., Kawamura, K., Chen, J., and Miyazaki, Y.: Secondary production of organic aerosols from biogenic VOCs over Mt. Fuji, Japan, Environ. Sci. Technol., 48, 8491–8497, https://doi.org/10.1021/es500794d, 2014.
Gelencsér, A., May, B., Simpson, D., Sánchez-Ochoa, A., Kasper-Giebl, A., Puxbaum, H., Caseiro, A., Pio, C. A., and Legrand, M.: Source apportionment of PM2.5 organic aerosol over Europe: Primary/secondary, natural/anthropogenic, and fossil/biogenic origin, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 112, 1–12, https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD008094, 2007.
He, Q. F., Ding, X., Fu, X. X., Zhang, Y. Q., Wang, J. Q., Liu, Y. X., Tang, M. J., Wang, X. M., and Rudich, Y.: Secondary organic aerosol formation from isoprene epoxides in the Pearl River Delta, South China: IEPOX- and HMML-derived tracers, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 123, 6999–7012, https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JD028242, 2018.
He, X., Huang, X. H. H., Chow, K. S., Wang, Q., Zhang, T., Wu, D., and Yu, J. Z.: Abundance and sources of phthalic acids, benzene-tricarboxylic acids, and phenolic acids in PM2.5 at urban and suburban sites in Southern China, ACS Earth Sp. Chem., 2, 147–158, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.7b00131, 2018.
Hildemann, L. M., Rogge, W. F., Cass, G. R., Mazurek, M. A., Simoneit, B. R. T.: Contribution of primary aerosol emissions from vegetation-derived sources to fine particle concentrations in Los Angeles, J. Geophys. Res., 101, 19541, https://doi.org/10.1029/95JD02136, 1996.
Hofzumahaus, A., Rohrer, F., Lu, K., Bohn, B., Brauers, T., Chang, C.-C., Fuchs, H., Holland, F., Kita, K., Kondo, Y., Li, X., Lou, S., Shao, M., Zeng, L., Wahner, A., and Zhang, Y.: Amplified trace gas removal in the troposphere, Science, 324, 1702–1704, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1164566, 2009.
Hu, D. and Yu, J. Z.: Secondary organic aerosol tracers and malic acid in Hong Kong: Seasonal trends and origins, Environ. Chem., 10, 381–394, https://doi.org/10.1071/EN13104, 2013.
Hu, D., Bian, Q., Li, T. W. Y., Lau, A. K. H., and Yu, J. Z.: Contributions of isoprene, monoterpenes, β-caryophyllene, and toluene to secondary organic aerosols in Hong Kong during the summer of 2006, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 113, D22206, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD010437, 2008.
Hu, D., Bian, Q., Lau, A. K. H., and Yu, J. Z.: Source apportioning of primary and secondary organic carbon in summer PM2.5 in Hong Kong using positive matrix factorization of secondary and primary organic tracer data, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 115, 1–14, https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD012498, 2010.
Huang, R. J., Zhang, Y., Bozzetti, C., Ho, K. F., Cao, J. J., Han, Y., Daellenbach, K. R., Slowik, J. G., Platt, S. M., Canonaco, F., Zotter, P., Wolf, R., Pieber, S. M., Bruns, E. A., Crippa, M., Ciarelli, G., Piazzalunga, A., Schwikowski, M., Abbaszade, G., Schnelle-Kreis, J., Zimmermann, R., An, Z., Szidat, S., Baltensperger, U., El Haddad, I., and Prevot, A. S.: High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China, Nature, 514, 218–222, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13774, 2014.
Ianni, J. C.: KINTECUS, Windows version 5.50, available at: http://kintecus.com (last access: 16 June 2021), 2015.
Jang, M., Czoschke, N. M., Lee, S., and Kamens, R. M.: Heterogeneous atmospheric aerosol production by acid-catalyzed particle-phase reactions, Science, 298, 814–817, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1075798, 2002.
Jaoui, M., Kleindienst, T. E., Lewandowski, M., Offenberg, J. H., and Edney, E. O.: Identification and quantification of aerosol polar oxygenated compounds bearing carboxylic or hydroxyl groups. 2. Organic tracer compounds from monoterpenes, Environ. Sci. Technol., 39, 5661–5673, https://doi.org/10.1021/es048111b, 2005.
Jokinen, T., Berndt, T., Makkonen, R., Kerminen, V. M., Junninen, H., Paasonen, P., Stratmann, F., Herrmann, H., Guenther, A. B., Worsnop, D. R., Kulmala, M., Ehn, M., and Sipilä, M.: Production of extremely low volatile organic compounds from biogenic emissions: Measured yields and atmospheric implications, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 112, 7123–7128, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1423977112, 2015.
Kanakidou, M., Seinfeld, J. H., Pandis, S. N., Barnes, I., Dentener, F. J., Facchini, M. C., Van Dingenen, R., Ervens, B., Nenes, A., Nielsen, C. J., Swietlicki, E., Putaud, J. P., Balkanski, Y., Fuzzi, S., Horth, J., Moortgat, G. K., Winterhalter, R., Myhre, C. E. L., Tsigaridis, K., Vignati, E., Stephanou, E. G., and Wilson, J.: Organic aerosol and global climate modelling: a review, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 5, 1053–1123, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-5-1053-2005, 2005.
Kautzman, K. E., Surratt, J. D., Chan, M. N., Chan, A. W. H., Hersey, S. P., Chhabra, P. S., Dalleska, N. F., Wennberg, P. O., Flagan, R. C., and Seinfeld, J. H.: Chemical composition of gas- and aerosol-phase products from the photooxidation of naphthalene, J. Phys. Chem. A, 114, 913–934, https://doi.org/10.1021/jp908530s, 2010.
Kenseth, C. M., Huang, Y., Zhao, R., Dalleska, N. F., Caleb Hethcox, J., Stoltz, B. M., and Seinfeld, J. H.: Synergistic O3+OH oxidation pathway to extremely low-volatility dimers revealed in â-pinene secondary organic aerosol, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 115, 8301–8306, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1804671115, 2018.
Kitanovski, Z., Grgiæ, I., Vermeylen, R., Claeys, M., and Maenhaut, W.: Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for characterization of monoaromatic nitro-compounds in atmospheric particulate matter, J. Chromatogr. A, 1268, 35–43, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.10.021, 2012.
Kleindienst, T. E., Jaoui, M., Lewandowski, M., Offenberg, J. H., Lewis, C. W., Bhave, P. V., and Edney, E. O.: Estimates of the contributions of biogenic and anthropogenic hydrocarbons to secondary organic aerosol at a southeastern US location, Atmos. Environ., 41, 8288–8300, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.06.045, 2007.
Kleindienst, T. E., Lewandowski, M., Offenberg, J. H., Jaoui, M., and Edney, E. O.: The formation of secondary organic aerosol from the isoprene + OH reaction in the absence of NOx, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 6541–6558, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-6541-2009, 2009.
Kleindienst, T. E., Jaoui, M., Lewandowski, M., Offenberg, J. H., and Docherty, K. S.: The formation of SOA and chemical tracer compounds from the photooxidation of naphthalene and its methyl analogs in the presence and absence of nitrogen oxides, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 12, 8711–8726, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-8711-2012, 2012.
Lee, A., Goldstein, A. H., Keywood, M. D., Gao, S., Varutbangkul, V., Bahreini, R., Ng, N. L., Flagan, R. C., and Seinfeld, J. H.: Gas-phase products and secondary aerosol yields from the ozonolysis of ten different terpenes, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 111, 1–18, https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD006437, 2006a.
Lee, A., Goldstein, A. H., Kroll, J. H., Ng, N. L., Varutbangkul, V., Flagan, R. C., and Seinfeld, J. H.: Gas-phase products and secondary aerosol yields from the photo-oxidation of 16 different terpenes, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 111, D17305, https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD007050, 2006b.
Lewandowski, M., Jaoui, M., Offenberg, J. H., Kleindienst, T. E., Edney, E. O., Sheesley, R. J., and Schauer, J. J.: Primary and secondary contributions to ambient PM in the midwestern united states, Environ. Sci. Technol., 42, 3303–3309, https://doi.org/10.1021/es0720412, 2008.
Lin, Y.-H., Zhang, Z., Docherty, K. S., Zhang, H., Budisulistiorini, S. H., Rubitschun, C. L., Shaw, S. L., Knipping, E. M., Edgerton, E. S., Kleindienst, T. E., Gold, A., and Surratt, J. D.: Isoprene epoxydiols as precursors to secondary organic aerosol formation: Acid-catalyzed reactive uptake studies with authentic compounds, Environ. Sci. Technol., 46, 250–258, https://doi.org/10.1021/es202554c, 2012.
Lin, Y.-H., Zhang, H., Pye, H. O. T., Zhang, Z., Marth, W. J., Park, S., Arashiro, M., Cui, T., Budisulistiorini, S. H., Sexton, K. G., Vizuete, W., Xie, Y., Luecken, D. J., Piletic, I. R., Edney, E. O., Bartolotti, L. J., Gold, A., and Surratt, J. D.: Epoxide as a precursor to secondary organic aerosol formation from isoprene photo-oxidation in the presence of nitrogen oxides, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, 6718–6723, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1221150110, 2013.
Lu, X. and Fung, J.: Source apportionment of sulfate and nitrate over the Pearl River Delta Region in China, Atmosphere, 7, 98, https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7080098, 2016.
Ma, Y., Cheng, Y., Qiu, X., Lin, Y., Cao, J., and Hu, D.: A quantitative assessment of source contributions to fine particulate matter (PM2.5)-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their nitrated and hydroxylated derivatives in Hong Kong, Environ. Pollut., 219, 742–749, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.07.034, 2016.
Ma, Y., Cheng, Y., Qiu, X., Cao, G., Fang, Y., Wang, J., Zhu, T., Yu, J., and Hu, D.: Sources and oxidative potential of water-soluble humic-like substances (HULISWS) in fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in Beijing, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 18, 5607–5617, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-5607-2018, 2018.
Ma, Y., Cheng, Y., Qiu, X., Cao, G., Kuang, B., Yu, J. Z., and Hu, D.: Optical properties, source apportionment and redox activity of humic-like substances (HULIS) in airborne fine particulates in Hong Kong, Environ. Pollut., 255, 113087, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113087, 2019.
Mancilla, Y., Herckes, P., Fraser, M. P., and Mendoza, A.: Secondary organic aerosol contributions to PM2.5 in Monterrey, Mexico: Temporal and seasonal variation, Atmos. Res., 153, 348–359, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.09.009, 2015.
Minerath, E. C., Casale, M. T., and Elrod, M. J.: Kinetics feasibility study of alcohol sulfate esterification reactions in tropospheric aerosols, Environ. Sci. Technol., 42, 4410–4415, https://doi.org/10.1021/es8004333, 2008.
Ng, N. L., Kwan, A. J., Surratt, J. D., Chan, A. W. H., Chhabra, P. S., Sorooshian, A., Pye, H. O. T., Crounse, J. D., Wennberg, P. O., Flagan, R. C., and Seinfeld, J. H.: Secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formation from reaction of isoprene with nitrate radicals (NO3), Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 4117–4140, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-8-4117-2008, 2008.
Nguyen, T. B., Bates, K. H., Crounse, J. D., Schwantes, R. H., Zhang, X., Kjaergaard, H. G., Surratt, J. D., Lin, P., Laskin, A., Seinfeld, J. H., and Wennberg, P. O.: Mechanism of the hydroxyl radical oxidation of methacryloyl peroxynitrate (MPAN) and its pathway toward secondary organic aerosol formation in the atmosphere, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 17, 17914–17926, https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cp02001h, 2015.
Offenberg, J. H., Lewis, C. W., Lewandowski, M., Jaoui, M., Kleindienst, T. E., and Edney, E. O.: Contributions of toluene and α-pinene to SOA formed in an irradiated toluene/a-pinene/NOx/air mixture: comparison of results using 14C content and SOA organic tracer methods, Environ. Sci. Technol., 41, 3972–3976, https://doi.org/10.1021/es070089, 2007.
Rattanavaraha, W., Chu, K., Budisulistiorini, S. H., Riva, M., Lin, Y.-H., Edgerton, E. S., Baumann, K., Shaw, S. L., Guo, H., King, L., Weber, R. J., Neff, M. E., Stone, E. A., Offenberg, J. H., Zhang, Z., Gold, A., and Surratt, J. D.: Assessing the impact of anthropogenic pollution on isoprene-derived secondary organic aerosol formation in PM2.5 collected from the Birmingham, Alabama, ground site during the 2013 Southern Oxidant and Aerosol Study, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 16, 4897–4914, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-4897-2016, 2016.
Riedel, T. P., Lin, Y. H., Budisulistiorini, S. H., Gaston, C. J., Thornton, J. A., Zhang, Z., Vizuete, W., Gold, A., and Surratt, J. D.: Heterogeneous reactions of isoprene-derived epoxides: Reaction probabilities and molar secondary organic aerosol yield estimates, Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett., 2, 38–42, https://doi.org/10.1021/ez500406f, 2015.
Riva, M., Tomaz, S., Cui, T., Lin, Y. H., Perraudin, E., Gold, A., Stone, E. A., Villenave, E., and Surratt, J. D.: Evidence for an unrecognized secondary anthropogenic source of organosulfates and sulfonates: Gas-phase oxidation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the presence of sulfate aerosol, Environ. Sci. Technol., 49, 6654–6664, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00836, 2015.
Roberts, J. M. and Bertman, S. B.: The thermal decomposition of peroxyacetic nitric anhydride (PAN) and peroxymethacrylic nitric anhydride (MPAN), Int. J. Chem. Kinet., 24, 297–307, https://doi.org/10.1002/kin.550240307, 1992.
Rollins, A. W., Pusede, S., Wooldridge, P., Min, K.-E., Gentner, D. R., Goldstein, A. H., Liu, S., Day, D. A., Russell, L. M., Rubitschun, C. L., Surratt, J. D., and Cohen, R. C.: Gas particle partitioning of total alkyl nitrates observed with TD-LIF in Bakersfield, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 118, 6651–6662, https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50522, 2013.
Sang, X. F., Chan, C. Y., Engling, G., Chan, L. Y., Wang, X. M., Zhang, Y. N., Shi, S., Zhang, Z. S., Zhang, T., and Hu, M.: Levoglucosan enhancement in ambient aerosol during springtime transport events of biomass burning smoke to Southeast China, Tellus B, 63, 129–139, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0889.2010.00515.x, 2011.
Schauer, J. J., Kleeman, M. J., Cass, G. R., and Simoneit, B. R. T.: Measurement of emissions from air pollution sources. 3. C1-C29 organic compounds from fireplace combustion of wood, Environ. Sci. Technol., 35, 1716–1728, https://doi.org/10.1021/es001331e, 2001.
Schauer, J. J., Rogge, W. F., Hildemann, L. M., Mazurek, M. A., Cass, G. R., and Simoneit, B. R. T.: Source apportionment of airborne particulate matter using organic compounds as tracers, Atmos. Environ., 41, 241–259, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.10.069, 2007.
Simoneit, B. R. T.: A review of biomarker compounds as source indicators and tracers for air pollution, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 6, 159–169, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02987621, 1999.
Simoneit, B. R. T., Medeiros, P. M., and Didyk, B. M.: Combustion products of plastics as indicators for refuse burning in the atmosphere, Environ. Sci. Technol., 39, 6961–6970, https://doi.org/10.1021/es050767x, 2005.
Surratt, J. D., Chan, A. W. H., Eddingsaas, N. C., Chan, M., Loza, C. L., Kwan, A. J., Hersey, S. P., Flagan, R. C., Wennberg, P. O., and Seinfeld, J. H.: Reactive intermediates revealed in secondary organic aerosol formation from isoprene, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107, 6640–6645, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0911114107, 2010.
Tsui, J. K. Y., Guenther, A., Yip, W. K., and Chen, F.: A biogenic volatile organic compound emission inventory for Hong Kong, Atmos. Environ., 43, 6442–6448, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.01.027, 2009.
Van Dingenen, R., Raes, F., Putaud, J. P., Baltensperger, U., Charron, A., Facchini, M. C., Decesari, S., Fuzzi, S., Gehrig, R., Hansson, H. C., Harrison, R. M., Hüglin, C., Jones, A. M., Laj, P., Lorbeer, G., Maenhaut, W., Palmgren, F., Querol, X., Rodriguez, S., Schneider, J., Ten Brink, H., Tunved, P., Tørseth, K., Wehner, B., Weingartner, E., Wiedensohler, A., and Wåhlin, P.: A European aerosol phenomenology-1: Physical characteristics of particulate matter at kerbside, urban, rural and background sites in Europe, Atmos. Environ., 38, 2561–2577, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.01.040, 2004.
Viana, M., Amato, F., Alastuey, A., Querol, X., Moreno, T., Dos Santos, S. G., Herce, M. D., and Fernández-Patier, R.: Chemical tracers of particulate emissions from commercial shipping, Environ. Sci. Technol., 43, 7472–7477, https://doi.org/10.1021/es901558t, 2009.
Vione, D., Maurino, V., Minero, C., and Pelizzetti, E.: Phenol photonitration upon UV irradiation of nitrite in aqueous solution II: Effects of pH and TiO2, Chemosphere, 45, 903–910, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00036-4, 2001.
Wang, G., Zhang, R., Gomez, M. E., Yang, L., Zamora, M. L., Hu, M., Lin, Y., Peng, J., Guo, S., Meng, J., Li, J., Cheng, C., Hu, T., Ren, Y., Wang, Y. Y., Gao, J., Cao, J., An, Z., Zhou, W., Li, G., Wang, J., Tian, P., Marrero-Ortiz, W., Secrest, J., Du, Z., Zheng, J., Shang, D., Zeng, L., Shao, M., Wang, W., Huang, Y., Wang, Y. Y., Zhu, Y., Li, Y., Hu, J., Pan, B., Cai, L., Cheng, Y., Ji, Y., Zhang, F., Rosenfeld, D., Liss, P. S., Duce, R. A., Kolb, C. E., Molina, M. J., Peng, J., Duan, L., Ji, Y., Marrero-Ortiz, W., An, Z., Huang, R., Zhang, R., Tie, X., Li, G., and Cao, J.: Persistent sulfate formation from London Fog to Chinese haze, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 113, 13630–13635, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1616540113, 2016.
Wang, S., Wu, D., Wang, X. M., Fung, J. C. H., and Yu, J. Z.: Relative contributions of secondary organic aerosol formation from toluene, xylenes, isoprene, and monoterpenes in Hong Kong and Guangzhou in the Pearl River Delta, China: an emission-based box modeling study, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 118, 507–519, https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JD017985, 2013.
Worton, D. R., Surratt, J. D., LaFranchi, B. W., Chan, A. W. H., Zhao, Y., Weber, R. J., Park, J.-H., Gilman, J. B., De Gouw, J., Park, C., Schade, G., Beaver, M. R., St. Clair, J., Crounse, J. D., Wennberg, P., Wolfe, G. M., Harrold, S., Thornton, J., Farmer, D., Docherty, K. S., Cubison, M., Jimenez, J. L., Frossard, A., Russell, L. M., Kristensen, K., Glasius, M., Mao, J., Ren, X., Brune, B., Browne, E. C., Pusede, S., Cohen, R. C., Seinfeld, J. H., and Goldstein, A. H.: Observational insights into high- and low-NOx aerosol formation from isoprene, Environ. Sci. Technol., 47, 11403–11413, https://doi.org/10.1021/es4011064, 2013.
Xie, B., Fung, J. C. H., Chan, A., and Lau, A.: Evaluation of nonlocal and local planetary boundary layer schemes in the WRF model, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 117, D12103, https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JD017080, 2012.
Xu, L., Guo, H., Boyd, C. M., Klein, M., Bougiatioti, A., Cerully, K. M., Hite, J. R., Isaacman-VanWertz, G., Kreisberg, N. M., Knote, C., Olson, K., Koss, A., Goldstein, A. H., Hering, S. V., de Gouw, J., Baumann, K., Lee, S.-H., Nenes, A., Weber, R. J., and Ng, N. L.: Effects of anthropogenic emissions on aerosol formation from isoprene and monoterpenes in the southeastern United States, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 112, 37–42, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1417609112, 2015.
Yu, J. Z., Huang, X.-F., Xu, J., and Hu, M.: When aerosol sulfate goes up, so does oxalate: Implication for the formation mechanisms of oxalate, Environ. Sci. Technol., 39, 128–133, https://doi.org/10.1021/es049559f, 2005.
Yu, L., Smith, J., Laskin, A., Anastasio, C., Laskin, J., and Zhang, Q.: Chemical characterization of SOA formed from aqueous-phase reactions of phenols with the triplet excited state of carbonyl and hydroxyl radical, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 14, 13801–13816, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-13801-2014, 2014.
Yuan, Z. B., Yu, J. Z., Lau, A. K. H., Louie, P. K. K., and Fung, J. C. H.: Application of positive matrix factorization in estimating aerosol secondary organic carbon in Hong Kong and its relationship with secondary sulfate, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 6, 25–34, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-6-25-2006, 2006.
Zhang, H., Yee, L. D., Lee, B. H., Curtis, M. P., Worton, D. R., Isaacman-VanWertz, G., Offenberg, J. H., Lewandowski, M., Kleindienst, T. E., Beaver, M. R., Holder, A. L., Lonneman, W. A., Docherty, K. S., Jaoui, M., Pye, H. O. T., Hu, W., Day, D. A., Campuzano-Jost, P., Jimenez, J. L., Guo, H., Weber, R. J., De Gouw, J., Koss, A. R., Edgerton, E. S., Brune, W., Mohr, C., Lopez-Hilfiker, F. D., Lutz, A., Kreisberg, N. M., Spielman, S. R., Hering, S. V., Wilson, K. R., Thornton, J. A., and Goldstein, A. H.: Monoterpenes are the largest source of summertime organic aerosol in the southeastern United States, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 115, 2038–2043, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1717513115, 2018.
Zhang, Q., Jimenez, J. L., Canagaratna, M. R., Allan, J. D., Coe, H., Ulbrich, I., Alfarra, M. R., Takami, A., Middlebrook, A. M., Sun, Y. L., Dzepina, K., Dunlea, E., Docherty, K., DeCarlo, P. F., Salcedo, D., Onasch, T., Jayne, J. T., Miyoshi, T., Shimono, A., Hatakeyama, S., Takegawa, N., Kondo, Y., Schneider, J., Drewnick, F., Borrmann, S., Weimer, S., Demerjian, K., Williams, P., Bower, K., Bahreini, R., Cottrell, L., Griffin, R. J., Rautiainen, J., Sun, J. Y., Zhang, Y. M., and Worsnop, D. R.: Ubiquity and dominance of oxygenated species in organic aerosols in anthropogenically-influenced Northern Hemisphere midlatitudes, Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL029979, 2007.
Zhang, T., Claeys, M., Cachier, H., Dong, S., Wang, W., Maenhaut, W., and Liu, X.: Identification and estimation of the biomass burning contribution to Beijing aerosol using levoglucosan as a molecular marker, Atmos. Environ., 42, 7013–7021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.04.050, 2008.
Zhang, Y. X., Shao, M., Zhang, Y. H., Zeng, L. M., He, L. Y., Zhu, B., Wei, Y. J., and Zhu, X. L.: Source profiles of particulate organic matters emitted from cereal straw burnings, J. Environ. Sci., 19, 167–175, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60027-8, 2007.
Zheng, M., Salmon, L. G., Schauer, J. J., Zeng, L., Kiang, C. S., Zhang, Y., and Cass, G. R.: Seasonal trends in PM2.5 source contributions in Beijing, China, Atmos. Environ., 39, 3967–3976, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.03.036, 2005.
Zheng, M., Zhao, X., Cheng, Y., Yan, C., Shi, W., Zhang, X., Weber, R. J., Schauer, J. J., Wang, X., and Edgerton, E. S.: Sources of primary and secondary organic aerosol and their diurnal variations, J. Hazard. Mater., 264, 536–544, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.10.047, 2014.
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Method
- Results
- Conclusions
- Appendix A: Kinetic model of loss of isoprene intermediates
- Appendix B: Calculation of particle acidity and total liquid water content
- Data availability
- Author contributions
- Competing interests
- Acknowledgements
- Financial support
- Review statement
- References
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Method
- Results
- Conclusions
- Appendix A: Kinetic model of loss of isoprene intermediates
- Appendix B: Calculation of particle acidity and total liquid water content
- Data availability
- Author contributions
- Competing interests
- Acknowledgements
- Financial support
- Review statement
- References